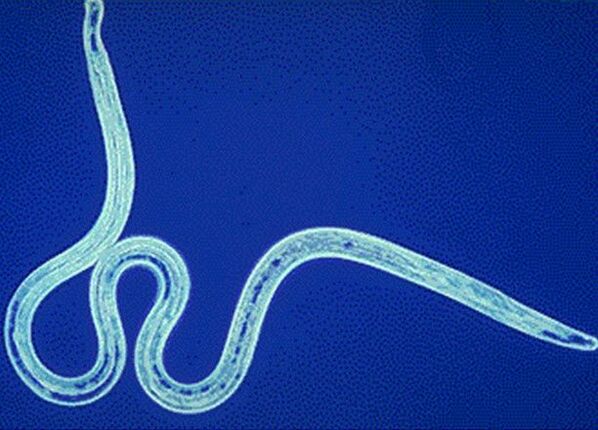
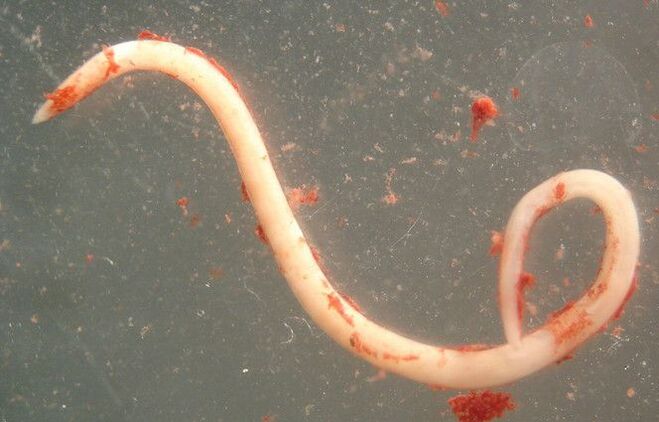
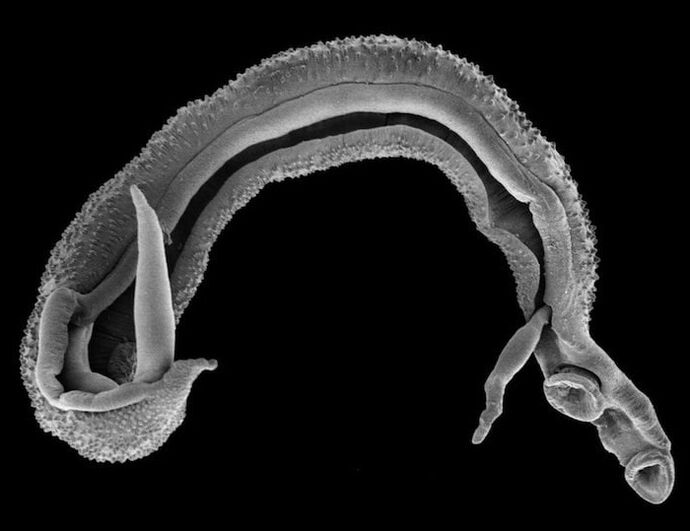
Parasites are referred to as lower organisms that can live in and feed on humans or animals. Scientists have a large collection of these organisms, each with its own dangers and potential for a variety of diseases.
Types of human parasites
All parasites can be differentiated according to several criteria:
- There are two broad categories that vary by body structure: unicellular (bacteria, viruses) and multicellular;
- Parasites can live on body surfaces (eg, lice) or inside organisms (eg, types of intestinal parasites: worms, etc. );
- Depending on how long they live: they can be permanent (almost all parasites that live in organisms) and temporary (leeches, mites, which leave the organism after being fed).

The most common parasites that humans can become infected with include:
- worm disease;
- protozoa invasive groups;
- Arthropod disease.
Helminthosis is the most common invader in the human body. These include roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes, which cause diseases such as flukes.
The 5 most famous parasites in the human body
- Pinworms - Most common in children. In humans, they live in organs such as the large and small intestines. The eggs she lays are not only inside her body, but can also be transferred to sheets and underwear, making her extremely contagious. Furthermore, these eggs are perfectly preserved in the external environment for a long time, although only 4-6 hours are needed for them to hatch new parasites.
- Toksokara - We most often get intruders from our beloved pets (mostly dogs). This creature is quite large - up to 0. 3 m in length. The parasite's eggs are most often "picked up" by children playing in the sandbox, where the dog walks around. This type of parasite is dangerous because it can penetrate almost all organs and the consequences of its life activities can be irreversible.
- Roundworms are a common parasite that infects more and more people every day. It most commonly enters the body along with unwashed food, raw water, dirty hands and dust. The parasite eggs that enter the body gradually begin to parasitize in the gut, which can then spread to other organs through blood vessels.
- Tapeworms are the largest of the most common parasites. Cases have been recorded when the extracted parasites reach several meters in length. The most common cause of infection is the consumption of salted fish, crayfish and caviar. If after that you find yourself experiencing worrisome symptoms, such as fatigue, increased drooling in the morning, nausea, and lethargy, you should see your doctor right away.
- Echinococcus can enter the human body through unwashed food, raw water, and animals. This parasite is dangerous because its larvae can spread to almost all organs. Gradually, they stop somewhere and turn into a cyst that begins to put pressure on nearby tissue.
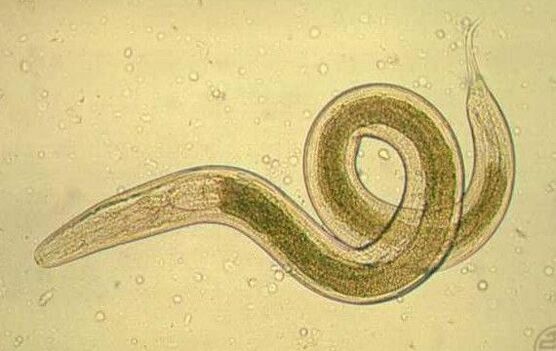
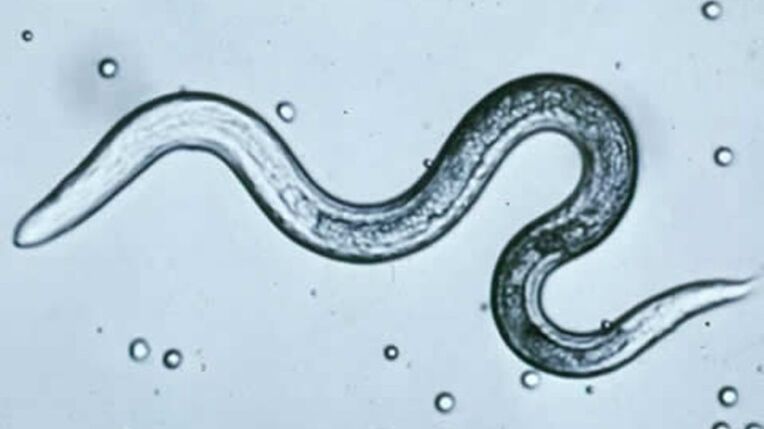
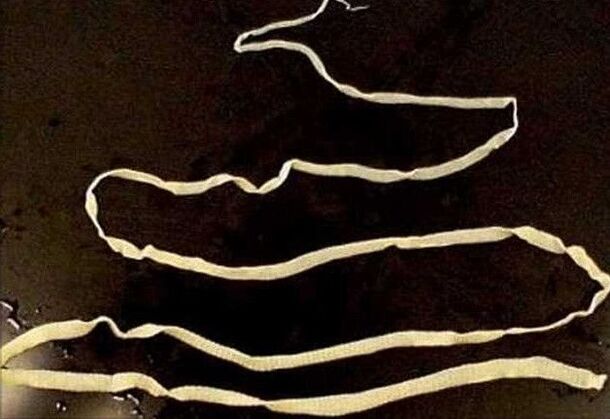
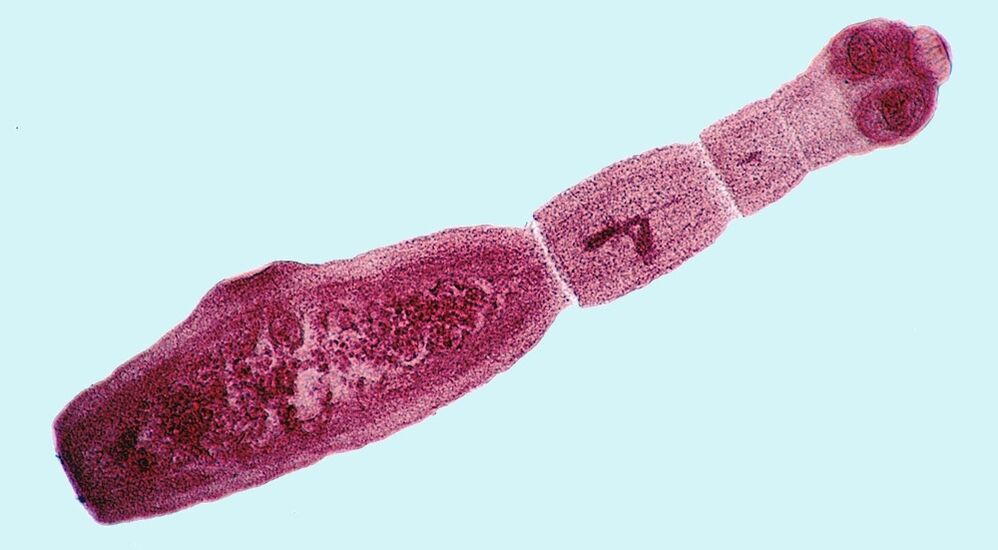
The most dangerous and rare parasites
In addition to the "traditional" parasites that are well known and easy to treat, there are many more dangerous and rare species. These include parasites such as:
- Bull Tapeworm - This parasite can live in the human body for almost a lifetime and is much larger than a tapeworm. According to scientists, on average, adult parasites can reach lengths of 4 to 40 meters.
- Filariasis is a more exotic parasite that can be found in tropical countries. Once in the body, it can cause the lymphatic vessels to become blocked, causing the limbs to begin to grow huge. This is the main reason for the development of "elephantia", as these parasites basically affect the lower extremities.
- Anisakid was recently discovered by scientists. Previously, it was reported that these parasites are not dangerous because they cannot develop in the human body. But these pests have now been shown to cause deadly diseases. Mostly, they enter the human body along with half-raw seafood and fish.
- Schistosomiasis - this guest cannot be picked up in everyday life, but when traveling somewhere in the tropics - this is rudimentary. Especially if you buy somewhere in fresh water in a hot tropical climate. Once in the body, they can cause anemia, depression and developmental delays, and reduced learning abilities.